- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
WHAT IS CAD/CAM IN DENTISTRY?

Introduction
Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technology systems utilize the use of computers to gather information and data, project and produce an extensive range of products. CAD/CAM, parts, and components can be premeditated and machined with precision using a computer with assimilated software linked to a milling device. The manufacturing industry has utilized computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) for decades to create precision tools and parts. The dental profession first adopted this technology in 1985, revolutionizing the construction of dental restorations and prostheses. Since then, CAD/CAM dentistry has only advanced, providing benefits to both professionals and patients.
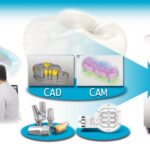
All about Digital Dentistry and the CAD/CAM Process
CAD/CAM dentistry describes the software that makes it possible for dental professionals to perform complex restorations faster, more efficiently, and sometimes more accurately. Both dental practices and laboratories use CAD/CAM technology to construct restorations like crowns, inlays, onlays, veneers, bridges, dentures, and implant-supported restorations from high-strength ceramic. Here’s what to expect from a restoration procedure using CAD/CAM.
- Tooth Preparation. Your dental professional will prepare the site for your restoration by removing all decay or portions of the structurally unsound tooth.
- Intraoral Scanning. Next, an optical scanner will digitally capture the tooth preparation and surrounding teeth to create a 3D custom image.
- Restoration Design. With those 3D images, the dental professional will use CAD software to design the final restoration.
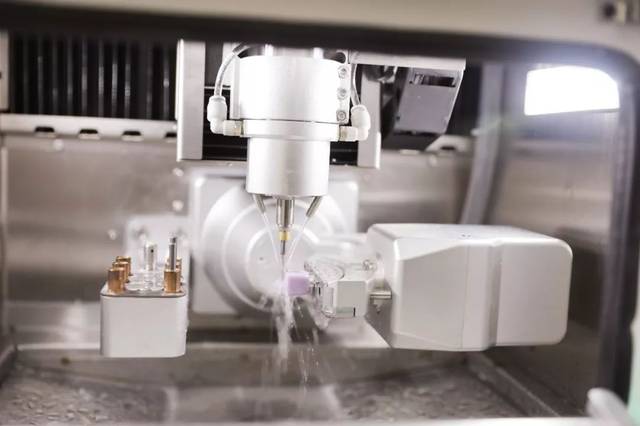
- Milling. Next, a milling machine takes the design and shapes the crown, veneer, inlay, onlay, or bridge with zirconia milling burs from a single block of ceramic.
- Sintering and Polishing. The restoration is stained or glazed to look more natural before being polished.
- Cementation. Finally, the restoration is permanently placed in your mouth to complete your smile.
This whole process could take anywhere from 45 minutes to two hours, depending on the case’s complexity. Still, CAD/CAM requires less time and effort than traditional laboratory methods.
- The Process
All CAD/CAM systems contain
- An optical scanner that captures the intraoral or extraoral condition
- Software that can turn the captured images into a digital model to produce and design the prosthesis
- A 3D technology that changes the data into a product
Normally the CAD/CAM dental restorations are milled from solid dental zirconia blank of ceramic or composite resin that closely match the basic shade of the restored tooth.
- Advantages of CAD/CAM in dentistry
The use of CAD/CAM technology provides benefits not only for dental professionals but also for patients. Some of the significant advantages include:
- Single-Visit Treatments. Using traditional laboratory methods, your dentist or prosthodontist would prepare your tooth, make an impression, and send the impression to a lab to create the final restoration. With CAD/CAM technology, the dental professional can sometimes complete all these steps in a single visit, allowing for fewer disruptions in your schedule.
- Digital Impressions. If you’ve ever had a conventional impression, you immediately understand the benefits of a digital system. The traditional method requires the patient to place a tray with a thick, gooey material — called alginate — in their mouth and hold for two to five minutes until the material sets. A scanner is placed in the patient’s mouth with digital impressions and moved around the affected area — like waving a magic wand.
- Cost-effectiveness. CAD/CAM technology eliminates several outsourcing costs for your dental professional, and these savings may be passed onto the patient. Be sure to ask about your options and the associated costs.
- Drawbacks of CAD/CAM Dentistry
- High initial Investment
It is a big financial investment as it involves purchasing multiple technologies such as the CAD/CAM system itself, a Cone Beam CT for 3-D imaging, and an optical scanner for digital impressions and accurate color analysis for staining. There’s also the cost of software updates, as well as restorative materials. This investment is risky as the professionals are not guaranteed of recovering their capital and making profits.to perfect their skills.
- Time on Training
The dentist has to familiarize and acquire knowledge and skills on how the CAD.CAM technology works. This means that much time will be taken on the training of dental experts and investment of money to allow the training to take place.
- Quality Concerns
Despite the CAD/CAM technology working out for many patients and good reviews and testimonials. There have been some quality concerns, this leaves the professionals to wonder whether or not to invest in this technology
- Does CAD/CAM Dental Work for Everyone?
Not every tooth can be treated with CAD/CAM dentistry, so talk to your dental professional about your best options. Because precision and fit are essential for your restoration or prosthesis, the practitioner may prefer using the conventional laboratory method for complex fabrications. Start by asking your dentist about CAD/CAM technology and how it may impact your restoration appointment.
- Dental Products
There is no need to crack your head on where you can purchase your dental equipment and supplies. Visit this website https://www.dentallaboratorio.com/product/dental-roland-zirconia-milling-burs and grab all materials you might need. There is a huge sale running at 70% off, so do not miss this chance Hurry Now and get all your dentist products.
Conclusion
The CAD/CAM systems have widely improved dentistry by providing high-quality restorations. This technology has evolved gradually by introducing user-friendly systems, have expanded capabilities, and most importantly improved quality. There are also new materials that have aesthetic features and are strong and durable.
We expect advancement in the future systems to improve on capability and efficiency, however, this might attract other costs such as training to boost the skills and knowledge of dentists. A major challenge that has not been addressed completely in existing systems is the completely automated, economical, high-precision production of restorations. High-speed machining is being adapted, allowing faster removal of material. This reduces machining time and could reduce production costs. The new technology it will allow phasing out of the challenges we face today. The future digitizers or scanners will be more robust ensuring accurate data is captured, henceforth the data will be sent directly to the CAD/CAM System without being interpreted by a technician.