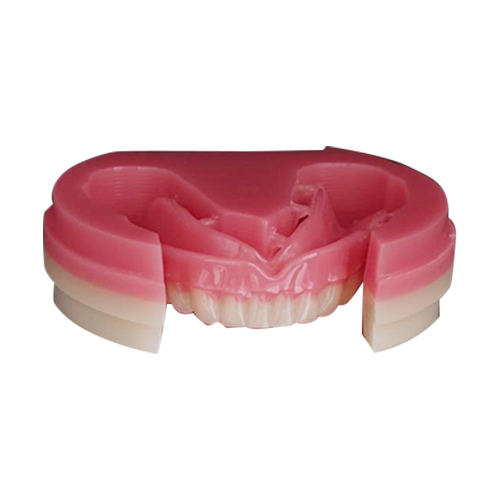
Pmma Dental Prosthesis In Dentistry
The Evolution of Dental Prosthetics: Understanding Monolayer and Multilayer PMMA
The fabrication of dental prostheses relies heavily on selecting the best suitable material. For decades, traditional dental prostheses utilized standard dental acrylic or metal for construction. While effective, these materials often presented challenges; many patients found it difficult to get used to the feel of new dentures, and some suffered severe allergic reactions, including irritation and soreness to oral tissues caused by the acrylic base.
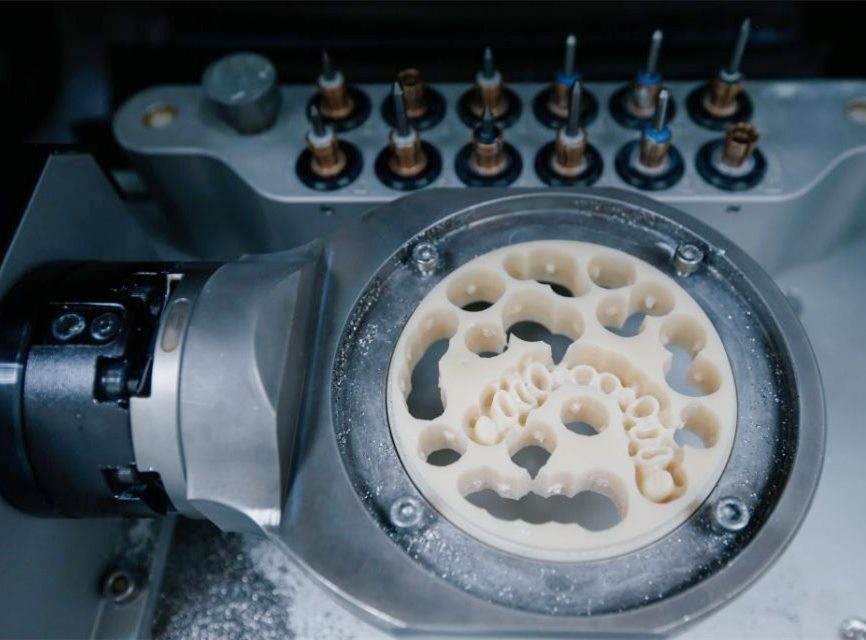
With new research and advancements in dental technology, a superior material has emerged as the standard for high-quality prosthetics: PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate). The prostheses are fabricated by digital CAD/CAM workflow with the PMMA block materials.

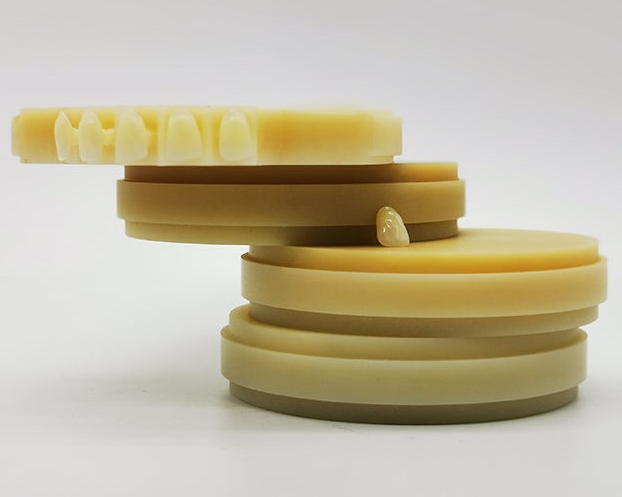
Today, dental PMMA is available in highly sophisticated forms, primarily Monolayer PMMA and Multilayer PMMA. These materials are colorless, translucent, and offer exceptional strength for the fabrication of various dental devices.
*Note on Material Accuracy: It is important to distinguish that PMMA is distinct from Acetal (Polyoxymethylene). While Acetal is often used for flexible applications, PMMA is a rigid, high-strength resin preferred for its aesthetic qualities and polishability.*
Monolayer vs. Multilayer PMMA
When laboratories utilize PMMA for modern restorations, they generally choose between two types of blocks based on the aesthetic requirements:
- Monolayer PMMA: This consists of a solid, uniform color throughout the block. It is characterized by high homogeneity and strength, making it an excellent choice for full denture bases and single-shade provisional crowns and bridges.
- Multilayer PMMA: This advanced material features different layers of color gradients. It mimics the natural transition of colors found in natural teeth (from the dentin body to the incisal edge) and provides a natural color saturation to the prostheses. It offers the same excellent toughness as monolayer PMMA but provides a superior, lifelike appearance.
The Digital Workflow: From Dentist to Laboratory
The application of PMMA has been revolutionized by CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing) technology. This digital workflow ensures precision and efficiency:
- Scanning: The dentist scans the patient’s mouth using an intraoral scanner.
- Sharing: The dentist shares the STL file directly with the dental laboratory.
- Design and Milling: The laboratory technician designs the prosthesis and uses a CAD/CAM machine to mill it out of a pre-formed PMMA block (Monolayer or Multilayer).
This procedure results in restorations with an excellent fit, reduced porosity, and fewer biological issues compared to traditional manually processed acrylics.
Advantages of PMMA in Dentistry
PMMA constructs lightweight and durable dental devices that are significantly more comfortable than conventional dentures. The specific advantages include:
- Biocompatibility: PMMA is biocompatible and insoluble in oral fluids like saliva. It significantly reduces the risk of allergic reactions compared to legacy materials.
- Strength and Stability: PMMA dentures are fracture-resistant and non-brittle. The material is dimensionally stable, meaning the prosthesis can bear mastication (chewing) forces without warping or changing shape.
- Aesthetics: PMMA provides a natural look to dental prostheses. The multilayer variations specifically allow for the visualization of natural hues and depth.
- Functionality: Chewing and phonetics (speech) are more convenient with PMMA dentures due to their accurate fit and lighter weight.
- Hygiene and Maintenance: PMMA has good bonding properties with artificial teeth and offers excellent oral hygiene. The surface is easy to polish and clean, and the material can be easily manipulated or repaired if necessary.
Applications of Dental PMMA
PMMA is widely used across various fields of dentistry due to its versatility:
- Prosthodontics: PMMA is the material of choice for the fabrication of denture bases and removable partial dentures.
- Restorative Dentistry: Both monolayer and multilayer PMMA are used to fabricate long-term temporary crowns and bridges (provisionals) and implant-supported superstructures.
- Orthodontics: PMMA is suitable for the fabrication of occlusal splints and night guards due to its rigidity and durability.
- Maxillofacial Surgery: The material is used to fabricate palatal obturators to close oro-nasal or oro-antral openings.
- Laboratory Utilities: Beyond patient-specific prosthetics, PMMA is used to construct accurate secondary impression trays and artificial acrylic teeth.
Need high-quality dental PMMA blocks? We offer monolayer and multilayer options in VITA 16 shades compatible with Zirkonzahn, Sirona, and Amann Girrbach systems. Explore our store for 98mm standard diameter blocks today.
Close Thoughts
Dental PMMA is an ideal material for prosthetics in both Monolayer and Multilayer forms. By leveraging CAD/CAM technology and the seamless transfer of STL files from dentist to laboratory, modern PMMA restorations ensure a diligent, high-end result. The combination of superior aesthetics, high strength, and biocompatibility makes PMMA the modern standard for patient comfort and long-lasting dental health.